The Role of Private Companies in Space Exploration
Various companies and the space industry are transforming space exploration. Discover the leaders and their advancements in the field.

There has been a giant change in the space business. Space exploration used to be exclusive for governments, but now private businesses like SpaceX and Blue Origin are changing the game.
The current space race is evolving quickly as billion-dollar companies and scruffy entrepreneurs compete. Costs for launching things have gone down a lot, and new ideas are coming up faster than before. The result makes space more accessible than ever.
This new age of commercial space is changing the sector and opening up new businesses, such as space tourism and satellite internet constellations.
The New Space Race: Companies Are Leading the Way
The present space race has turned into a competition where private corporations are in the lead. Countries are trying harder than ever to gain an edge in space, which is becoming more important in politics and the economy. A top industry analyst stated, “The new space race isn’t just about getting to the moon or Mars before someone else; it’s also about making a long-term presence in space.”
The first space race primarily involved governments, with superpowers competing against each other. But in today’s space race, billionaires with rockets are competing with government space projects. When NASA halted its Space Shuttle program in 2011, it created a gap that other businesses quickly filled, changing how people go to space forever.
1. From a government monopoly to competition in business
The shift from a government monopoly to market competition has sped up innovation so much that conventional aerospace contractors would require smelling salts. Innovations like reusable rockets have cut launch costs by up to 90%, making space more accessible than a celebrity’s own island.
- Private businesses are pushing the space sector to come up with new ideas.
- New chances for space exploration have come up since launch prices have gone down.
- Businesses are establishing new markets, such as space tourism and factories that make things in orbit.
2. The Effect on the Economy of Commercial Space Ventures
In 2019, commercial space enterprises made an estimated $424 billion, and many think the business might reach $1 trillion by 2040. The economic impacts go beyond the firms themselves. They provide high-skilled employment and encourage technical advances that help land-based sectors.
Governments still play important roles in space exploration, but they are becoming more like consumers than the only ones in charge of space operations. As the sector grows, it’s evident that private enterprises will be there for a long time. They are expanding the frontiers of space exploration and fostering the generation of innovative ideas.
Companies and Space: How the Private Sector is Changing Space Exploration
Governments used to be the only ones that explored space, but today private enterprises are becoming important actors. Space commercialization started decades ago, but it has sped up a lot in the last several years. Today, companies are involved in every aspect of the space business, ranging from rocket launches to satellite manufacturing and even mining asteroids.
The shift lies not only in the number of firms involved but also in the innovative ideas they contribute. The private sector has instilled a “move fast and break things” mindset in an industry previously known for its meticulousness and thoroughness.
1. The Commercialization Schedule
The Telstar 1 satellite, the first private communications satellite, was launched in the 1960s. This was the first time space was used for business. The contemporary commercial space era didn’t really take off until the 2000s, when NASA started pushing private businesses to build systems for transporting goods and people.
- The first commercial use of space was Telstar 1 in the 1960s.
- NASA’s support in the 2000s led to the growth of commercial cargo and personnel transport.
- Today, there are many different firms in the space sector that provide a wide variety of services.
2. Different kinds of space companies and what they do
There are presently several types of space enterprises, such as launch providers, satellite makers and operators, space tourist companies, research platforms, and resource utilization pioneers. The aerospace business is full of competition and life because big companies like Boeing and Lockheed Martin work with little entrepreneurs.
The fact that the space sector is so diverse shows how quickly it is changing. Companies are pushing tech limits and making space more accessible to smaller nations and businesses.
- Launch providers are changing the way people go to space.
- Satellite makers and operators are crucial for communications and watching the Earth.
- Space tourism companies are making it possible for regular people to go to space.
Launch Vehicle Manufacturers: The Way to Get to Space
Launch vehicle makers control the path into space. Their rockets are the only way to get into orbit. These corporations are the cosmic gatekeepers, giving us the important tools we need to explore space.
1. SpaceX: Changing the Economics of Launches
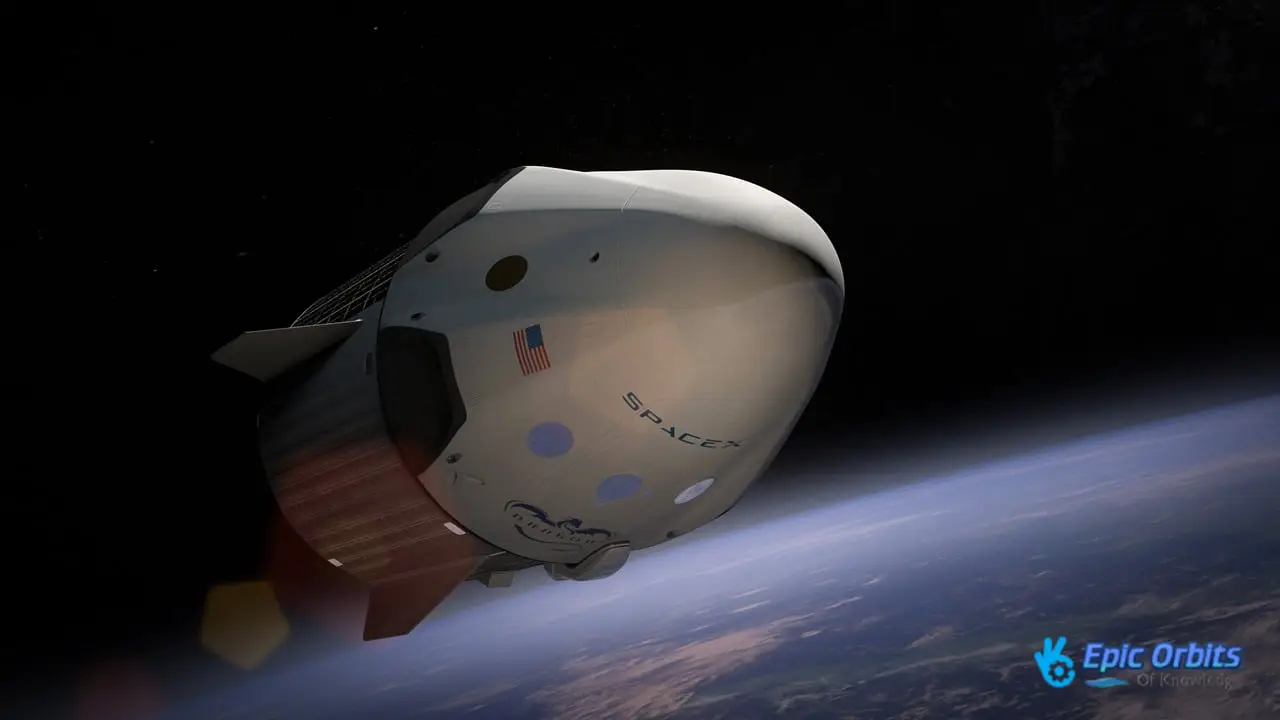

SpaceX’s reusable rockets have changed the launch business and made it cheaper to go to space. The Falcon 9 rocket from the business has become a workhorse, sending up all kinds of cargo, such as commercial satellites, national security assets, and humans.
SpaceX charges around $67 million for each launch, which is a lot less than its rivals. This is because it can reuse the rocket and fairing parts, which make up 70% of the cost.
2. The Established Player: United Launch Alliance (ULA)
United Launch Alliance is a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin that manufactures launch vehicles in the conventional way. ULA’s rockets have sent important national security assets into space, but their exorbitant prices have rendered them less competitive in the current age.
ULA’s Atlas V rocket has been utilized for many important missions, although it costs a lot more than SpaceX’s rockets.

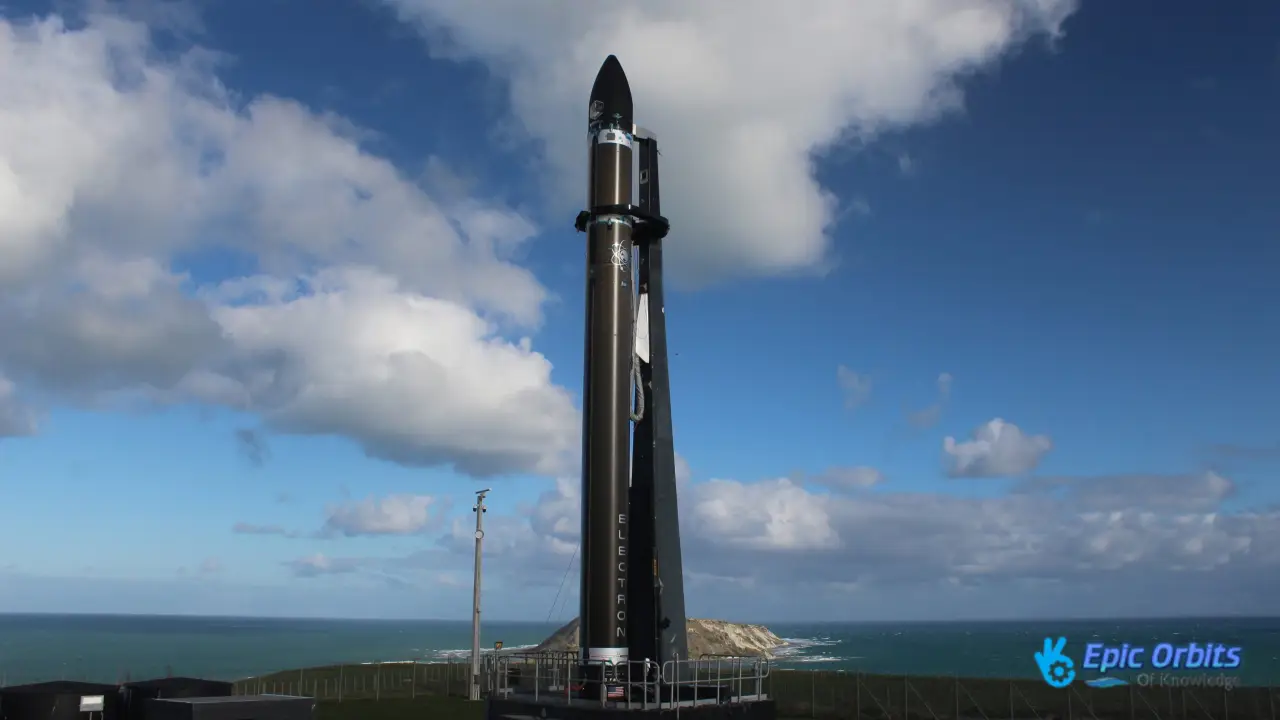
3. Rocket Lab: Experts in Small Satellites
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket has helped the company find a niche in the small satellite launch business. The company’s unique way of doing things has made it a big player in the launch business.
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket has successfully sent many tiny satellites into orbit, making it a dependable and cost-effective option for small satellite owners.

The market for launch vehicles is becoming more and more competitive, thanks to businesses like SpaceX, ULA, and Rocket Lab, who are coming up with new ideas and lowering prices. These firms will be crucial in the future of space exploration since the need for launch services is only going to expand.
Cargo Transport Innovators: Bringing Goods to the Final Frontier
The demands of the International Space Station are as wide-ranging as they are large. It requires cargo ships that can carry anything from food to research experiments. It is challenging to keep the ISS supplied, and it takes special spacecraft that can handle the extreme conditions of space travel.
Innovators in cargo transport have responded to the challenge by creating innovative vehicles that can bring cargo to the ISS and bring back experimental data or trash. This skill is essential for keeping the space station up and running and for doing research.
1. SpaceX Dragon: The Ship That Can Be Used Again
The Dragon capsule from SpaceX has changed the way cargo is sent to orbit by becoming the first commercial spaceship to travel to the ISS and bring back a lot of stuff to Earth. It can transport both pressurized and unpressurized freight since it can hold 6,000 kg. The Dragon’s capacity to reuse and return cargo has significantly enhanced the efficiency of space travel.
2. Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus: A Reliable Way to Deliver
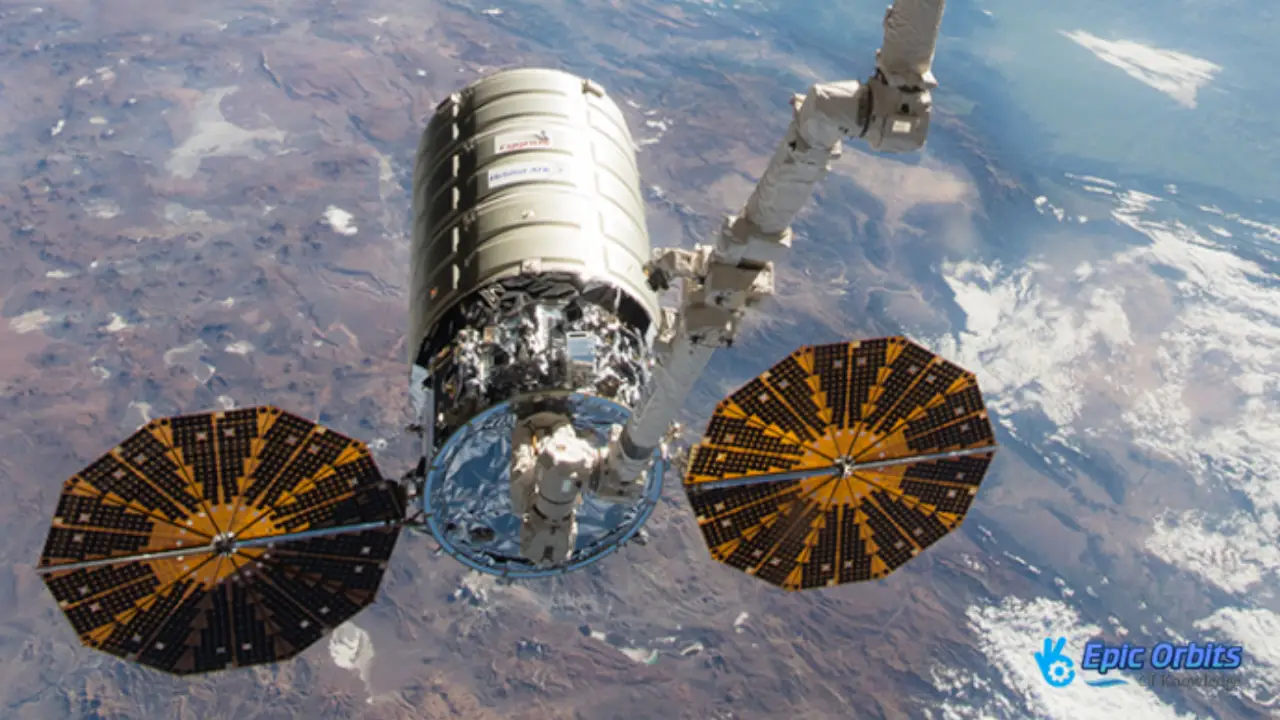

Another important spacecraft that brings goods to the ISS is Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus. Cygnus, which means “swan” in Latin, routinely brings hundreds of pounds of cargo to the space station, which keeps it running. Cygnus is vital to ISS logistics, even if it’s less reusable than Dragon.
SpaceX and Northrop Grumman are two companies that compete to offer cargo services. This has led to new ideas, lower prices, and NASA being able to concentrate on exploring deeper space. These cargo ships have turned into advanced research platforms that can deploy miniature satellites or experimental pallets from the outside. The success of these commercial cargo missions has made it possible for private enterprises to execute important space infrastructure tasks, which has led to the development of commercial crew transportation.
The role of freight transport innovation will always be important as the space industry changes. The future of space travel looks bright, thanks to firms like SpaceX and Northrop Grumman. These developments will allow for more ambitious missions and help us learn more about space.
Vehicles for transporting crew: Taking people to space
NASA’s money spent on commercial crew transport has opened the door for a new generation of people to fly to space. Making crew transport vehicles is a big step in making space more accessible to people.
NASA had to use Russian spacecraft to transfer people to the International Space Station when the Space Shuttle stopped flying in 2011. But this reliance has gone down a lot with the start of commercial crew programs.
1. NASA’s Commercial Crew Partner is SpaceX Crew Dragon.
The Crew Dragon from SpaceX has changed the space sector for the better. In 2020, it became the first commercial spaceship to take people into orbit, which was a big step forward in space exploration.
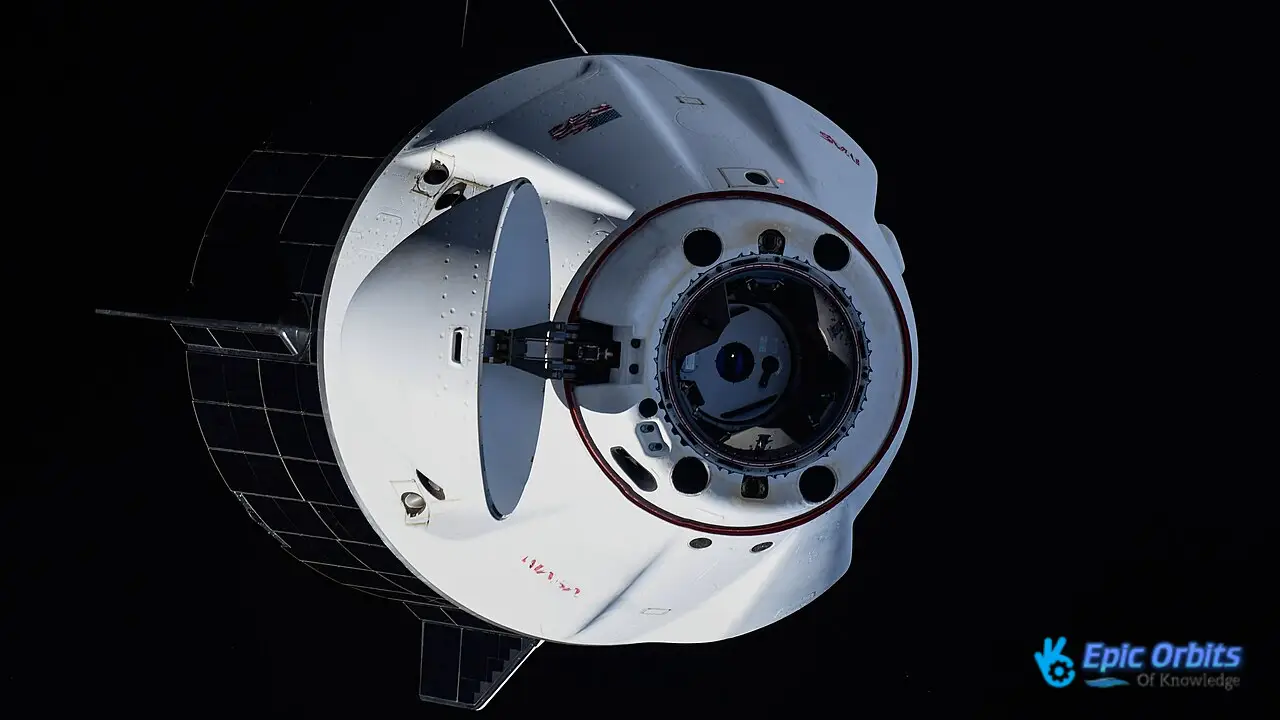

Astronauts love Crew Dragon’s elegant cabin, which incorporates touchscreens. Getting Netflix to function on the trip is still a problem, however.
2. Boeing Starliner: The Second Option for Commercial Crew
Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, often known as the Starliner, is another important part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner has completed uncrewed test flights, even though it had significant problems with its software and valves throughout development.
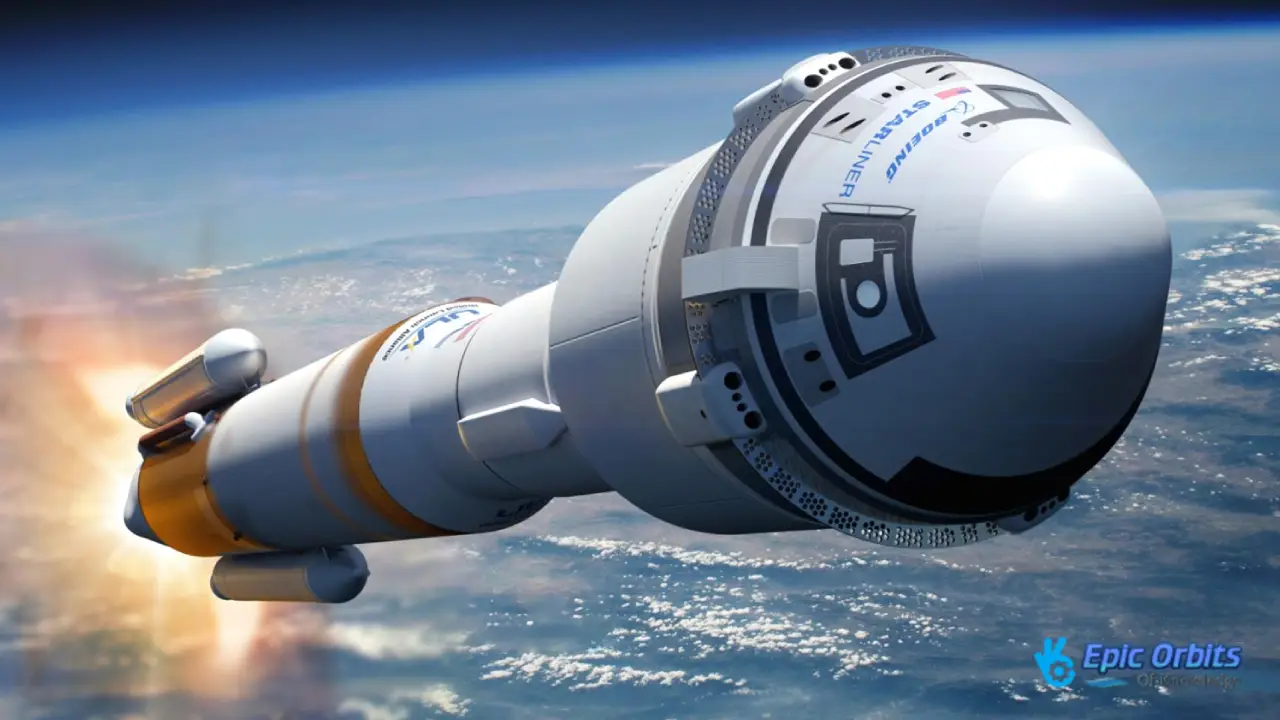

NASA has two ways to get humans to and from space because of the rivalry between SpaceX and Boeing. This means that astronauts won’t be stuck if one method has issues. Both Crew Dragon and Starliner are designed to dock with the International Space Station on their own, but they may also be controlled by a person if required.
NASA’s Commercial Crew Program is a big change in how the US does human spaceflight. It changes the agency from an operator to a customer. These new spacecraft meet 21st-century safety criteria and allow for aborts at any point during the launch procedure.
Space Tourism: Making Space Open to Everyone
The space tourism business has finally taken off, and regular people may now experience the excitement of traveling through space. Private enterprises are driving the way in this new area, with Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin at the top.
Space tourism has gone from being a concept in science fiction to an actual thing, enabling those with enough money to see the overall effect for themselves. The “billionaire space race” has started since these firms are competing with each other. Branson and Bezos both flew on their spaceships in 2021.
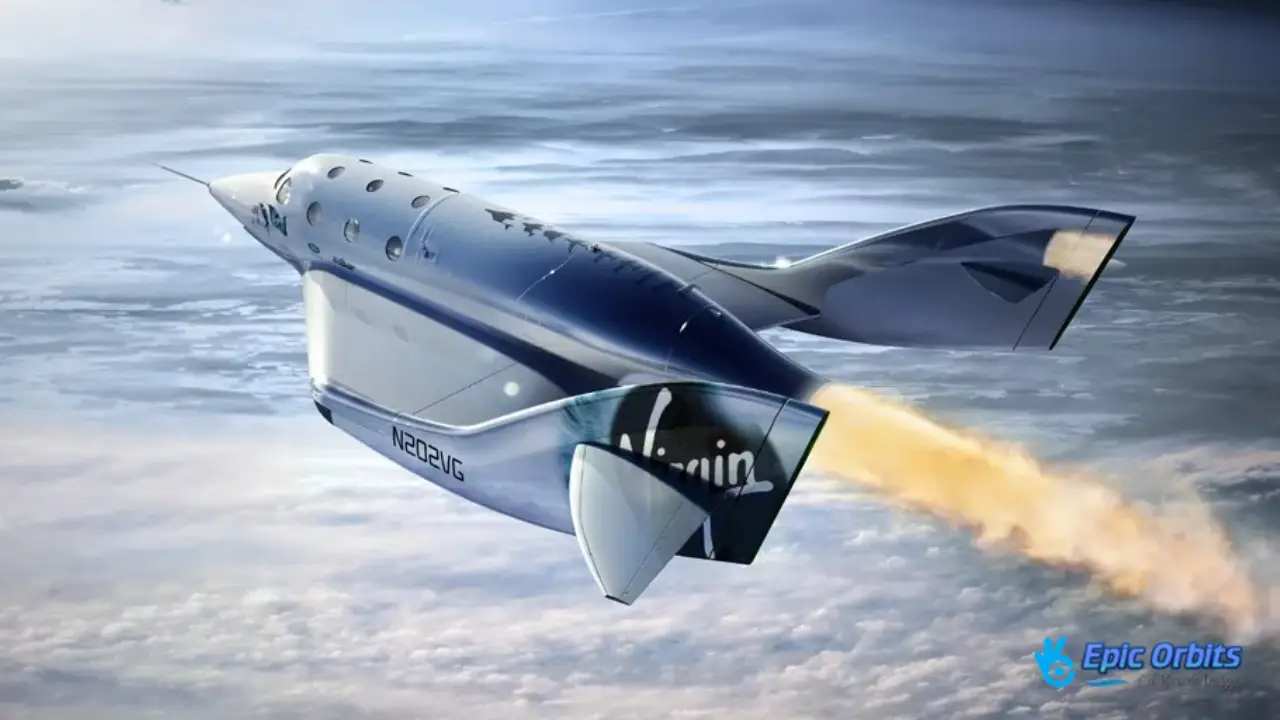
1. The First People to Go on Suborbital Trips
Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic has been a leader in the air-launched spaceplane method of space travel. Scaled Composites’ creation of SpaceShipOne marked a significant advancement in this project.

2. Trying to get tourist money
Blue Origin’s New Shepard, named after Alan Shepard, the first American astronaut, is a more conventional rocket that sends visitors straight up to just over the Kármán line, which is the widely acknowledged edge of space.
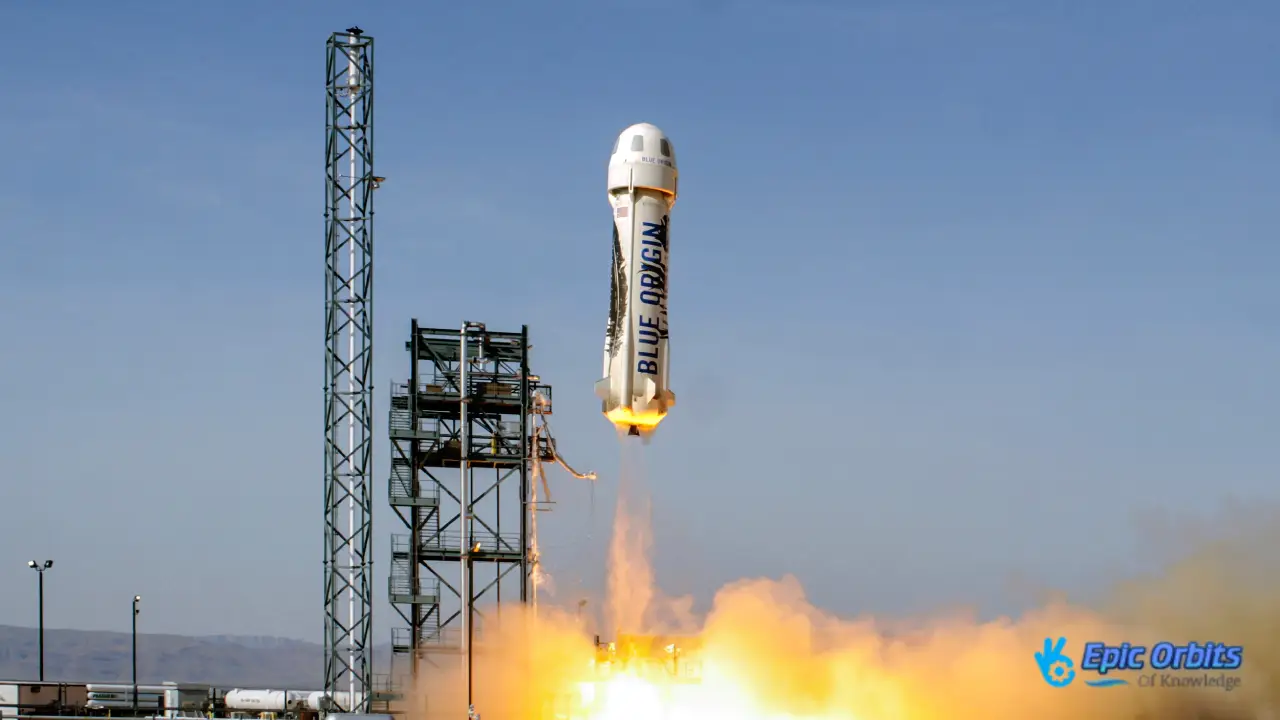

Space tourism is still the most luxurious thing you can do, even if it costs between $250,000 and $450,000 for each ticket. Even though they are costly, there are thousands of people on waiting lists for these suborbital joyrides. This data shows that people would pay nearly anything to pretend they have gone to space.
These tourist flights show off new technology and make money for firms that want to go beyond suborbital trips. The money they make helps pay for the construction of more sophisticated spacecraft. Critics say that space tourism is bad for the environment and doesn’t have a clear purpose. Supporters say that it gets people excited about space exploration and pushes technology forward.
Satellite Makers and Operators: Watchers in the Sky
A complicated network of satellites circles the Earth in the vastness of space. These satellites allow people worldwide to communicate and see what’s happening. These satellites are the backbone of our connected world. They send out everything from TV shows to weather forecasts, GPS navigation, and military information.
1. SES: A leader in global communications
SES is a big player in the satellite business, with more than 70 satellites in two distinct orbits. It says it reaches almost a billion individuals throughout the globe and provides network services to 58 government agencies. SES sells its connections to several businesses, including those in energy, cruise ships, aviation, and the military.

2. Maxar Technologies: Experts in Observing Earth
Maxar Technologies is well-known for its high-resolution imaging satellites, which take pictures of Earth in amazing detail. The company’s satellites can now take pictures with a resolution of 15 cm, which means that analysts can see things as tiny as a laptop from orbit. This capacity has big effects on both business and government uses.
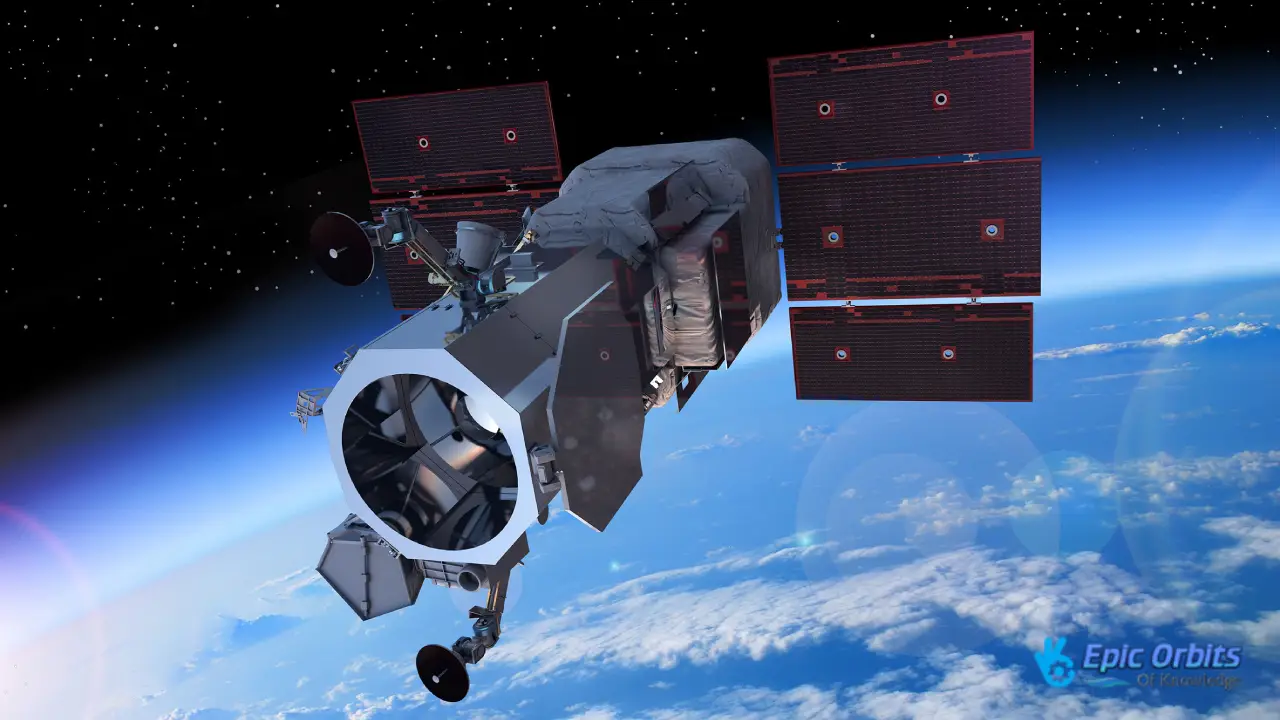

The commercial satellite sector has made space-based data more accessible to everyone. Now, smaller governments and businesses may buy images and services instead of having to create their own satellite networks. As satellite technology becomes better, the border between what the government and private enterprises may do gets less clear. Private businesses, for instance, now offer services that were previously exclusive to espionage organizations.
The New Satellite Internet Revolution: Starlink
SpaceX’s Starlink is redefining satellite internet with its mega-constellation strategy. Starlink is changing the way we go online by sending thousands of satellites into space. This makes the internet quicker and easier to get to, even in rural regions.
1. SpaceX’s Mega-Constellation: Changing How People Connect Around the World
With plans to launch up to 42,000 satellites, Starlink may be the most ambitious commercial space project ever. It will effectively establish the internet’s backbone in orbit. The mega-constellation technique puts hundreds of satellites in low Earth orbit, creating a cosmic mesh network that brings high-speed internet to even the most distant regions on Earth.
By the middle of 2023, SpaceX had already sent around 5,000 Starlink satellites into space. This is more than half of all the satellites that are currently circling Earth. This initiative has changed the satellite internet world and made it easier for people all around the world to connect.
2. Problems and issues with satellite constellations
While Starlink has the potential to change the world, it also faces significant problems and challenges. Astronomers are speaking out more and more about their worries because Starlink satellites may block optical and radio astronomy, leaving streaks in the night sky.
Regulations haven’t kept pace with the rapid launch of these massive satellite constellations into orbit. This raises concerns about how to control space traffic and the possibility of many collisions. However, Starlink has shown its worth in times of crisis by connecting people in conflict zones and countries hit by disasters like Ukraine.
Starlink’s success has started a new space race. Companies like Amazon’s Project Kuiper, OneWeb, and China’s GuoWang are all working on their own mega-constellations, which may place tens of thousands more satellites in orbit. It’s evident that Starlink is leading the way in the satellite internet revolution as it continues to change.
The lunar terrain will alter a lot as private firms like Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and ispace lead the way in exploring the moon. These firms are now paving the way for a return to the Moon after decades of neglect following the Apollo program.
3. NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services: Astrobotic and Intuitive Machines
The Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative from NASA has opened up a new age of exploring the moon. Astrobotic and Intuitive Machines are two companies that are trying to get scientific tools to the surface of the Moon. These commercial lunar landers are not only cheaper, but they also enable a greater frequency and variety of Moon missions.
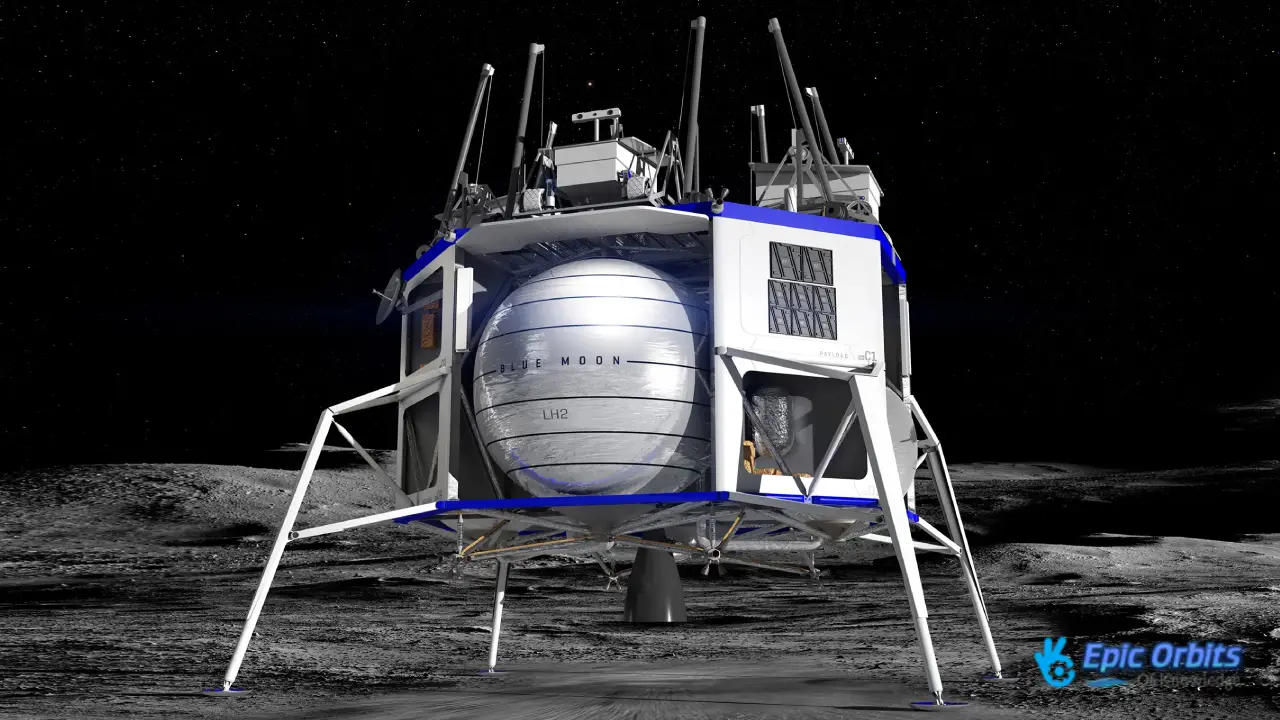

The CLPS initiative is a big change in how we explore space. It enables private enterprises to construct projects that were previously the responsibility of major governments. Astrobotic and Intuitive Machines are leading the way in this initiative, with the goal of becoming the first commercial businesses to land on the Moon.
4. ispace: Japan’s Plans for the Moon
ispace, a business established in Japan, has its eyes set on the Moon. They want to land on it, investigate it, and ultimately build a human community there. Even though their first expedition crashed on the moon’s surface in April 2023, ispace is still determined to build “Moon Valley,” a big metropolis on the moon.
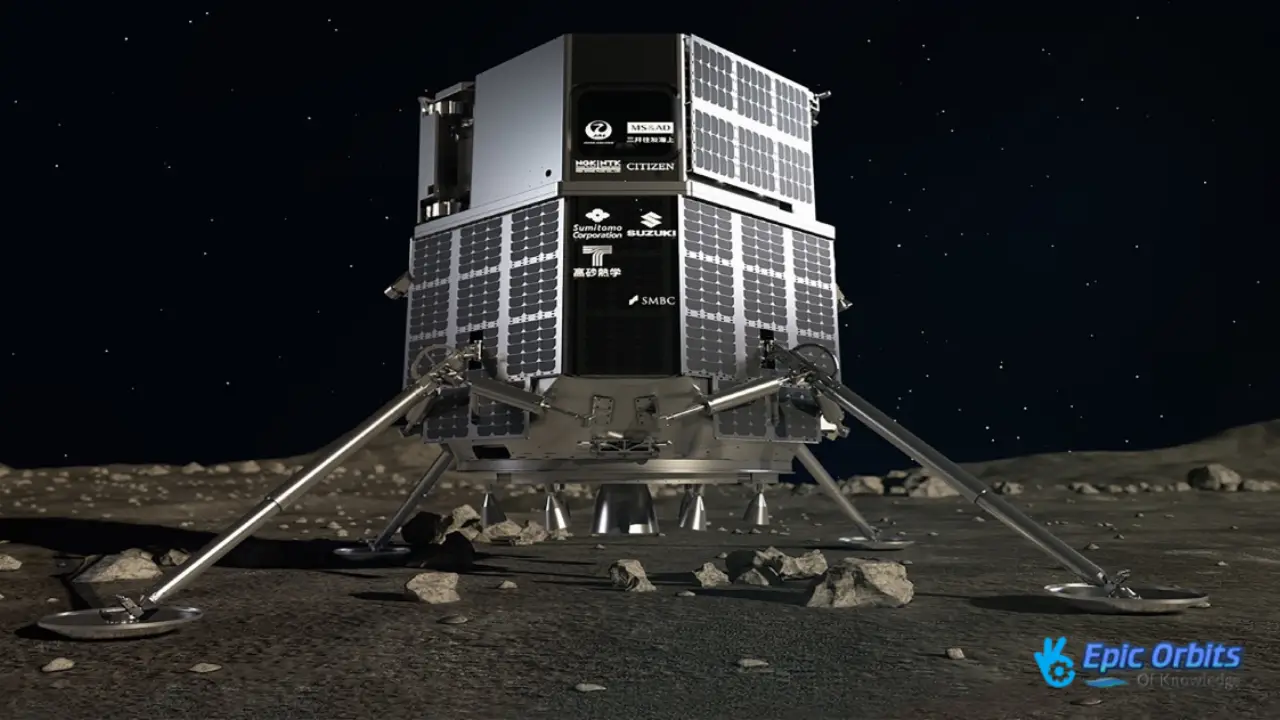

The company’s future missions are bigger and more difficult. They plan to dispatch rovers to the moon in search of resources for establishing a colony. Space wants to conquer the hurdles of landing on the moon and exploring there, which shows how quickly space exploration is changing.
There is a lot of competition among commercial businesses for being the first to arrive on the moon. These companies are not only helping us learn more about the Moon, but they are also making it possible for humans to go there and beyond in the future.
Private Companies Want to Go Deep into Space, Starting with Mars
Private enterprises, with Mars as their primary objective, are propelling humanity towards the next significant milestone. While lunar missions are a logical next step in space exploration, several private businesses are aiming for the ultimate goal: Mars and beyond.
1. SpaceX’s Starship: The Ship to Mars
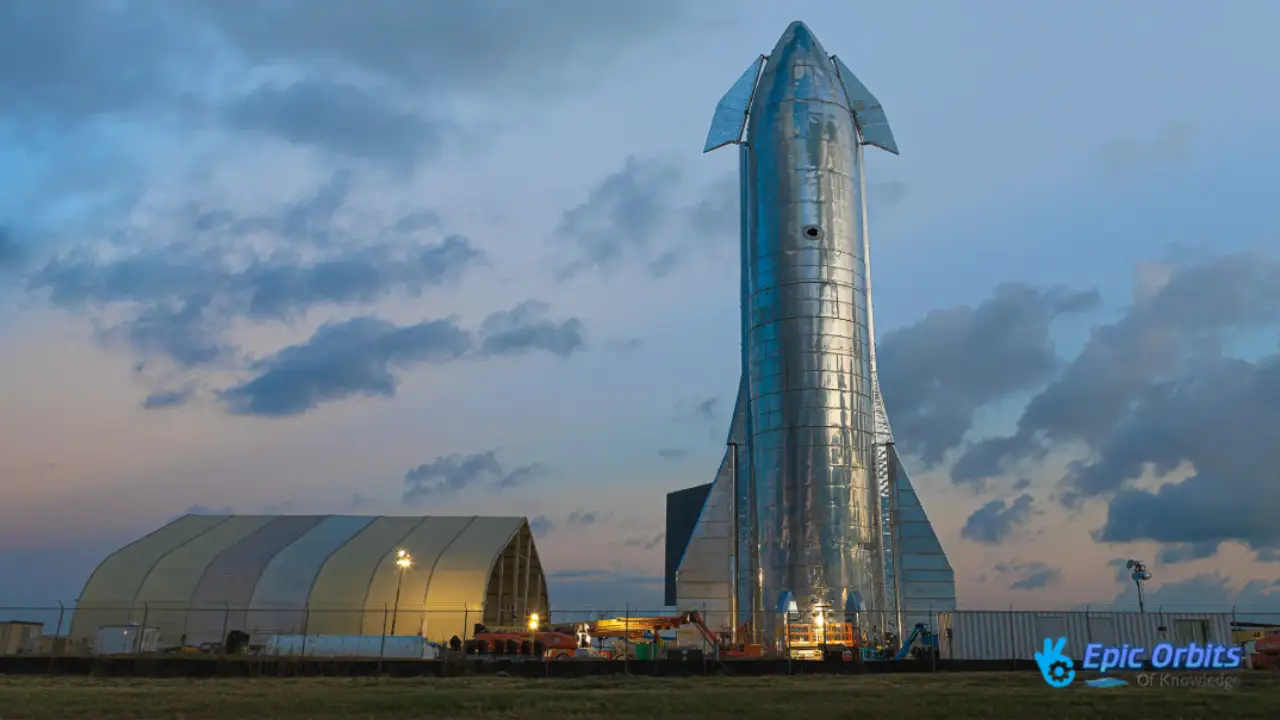

The Starship from SpaceX is the biggest and most ambitious spaceship ever built. It can take up to 100 people to Mars with the objective of building a city there that can support itself. Elon Musk’s concept for Mars appears improbable. He wants to send 1,000 Starships to Mars in sync with the right time windows, making a cosmic wagon train to the red planet.
Building Starship is a big step toward making it possible to explore deep space. The Starship’s reusability and capacity to carry a vast amount of cargo will forever transform the space business.
2. Blue Origin’s long-term goals
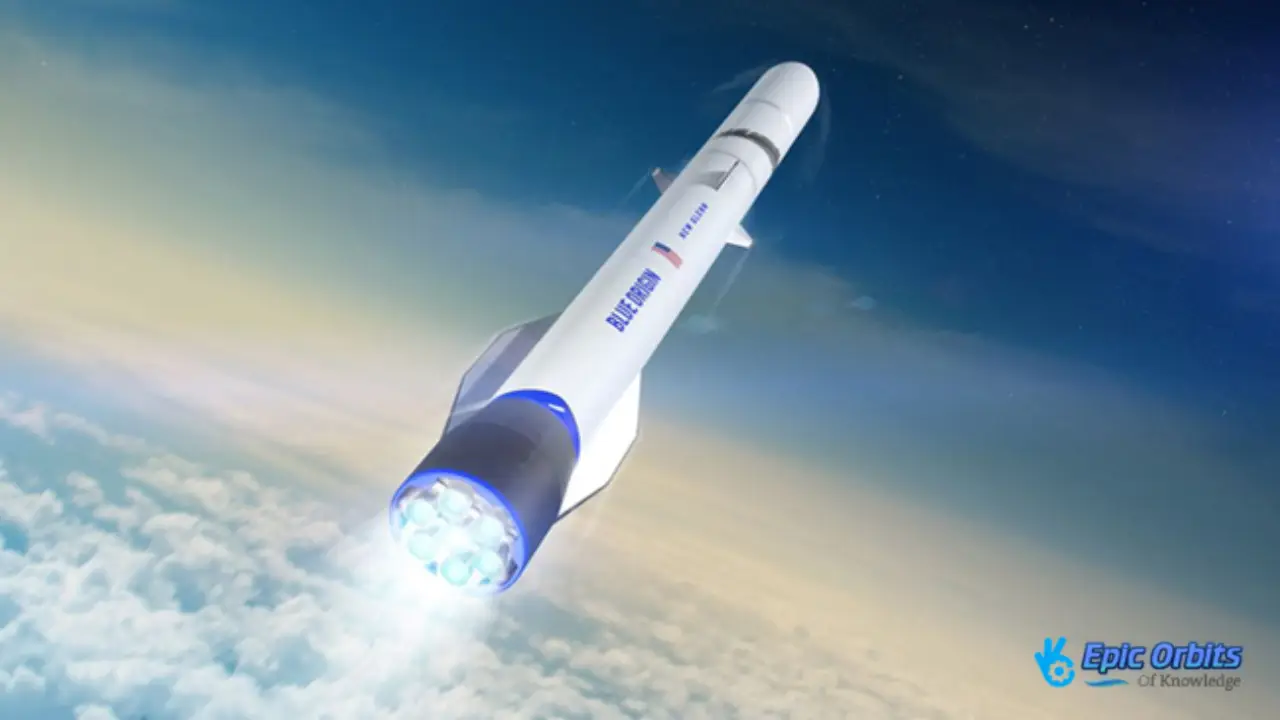

Blue Origin doesn’t talk about Mars as much, but creator Jeff Bezos has spoken of orbiting habitats that would make the International Space Station seem like a studio apartment. He has a long-term vision of millions of people living and working in space. To achieve these goals in deep space, we need to solve huge technological problems like protecting against radiation, providing closed-loop life support systems, using resources on-site, and giving psychological support to isolated workers.
The competition among deep space pioneers has accelerated technological progress and captured public interest in ways that government space projects cannot match. Both companies are developing technologies that can be used to explore the Moon and Mars. These technologies will assist them in accomplishing their most ambitious objectives.
Research and manufacturing in space
Private businesses are leading the way into a new area of space: using orbit for research and production that can’t be done on Earth. Space provides a unique environment for conducting scientific studies and producing materials that are not possible on Earth due to its microgravity, vacuum, and severe temperatures.
1. SpacePharma: Leading the Way in Microgravity Drug Research
SpacePharma is an Israeli firm that has been getting a lot of attention in the realm of space research by giving scientists the tools they need to conduct experiments in space. Their “labs” are designed to fit into regular experiment racks on the International Space Station (ISS), making it easier to do research in fields like biology, pharmaceuticals, and fluid physics. SpacePharma has been involved in many investigations on the ISS since 2017. Some of these experiments looked at how microgravity affects motor neuron cells and how asthma medicine crystallizes.
2. Space Forge: Changing the Way Things Are Made in Space
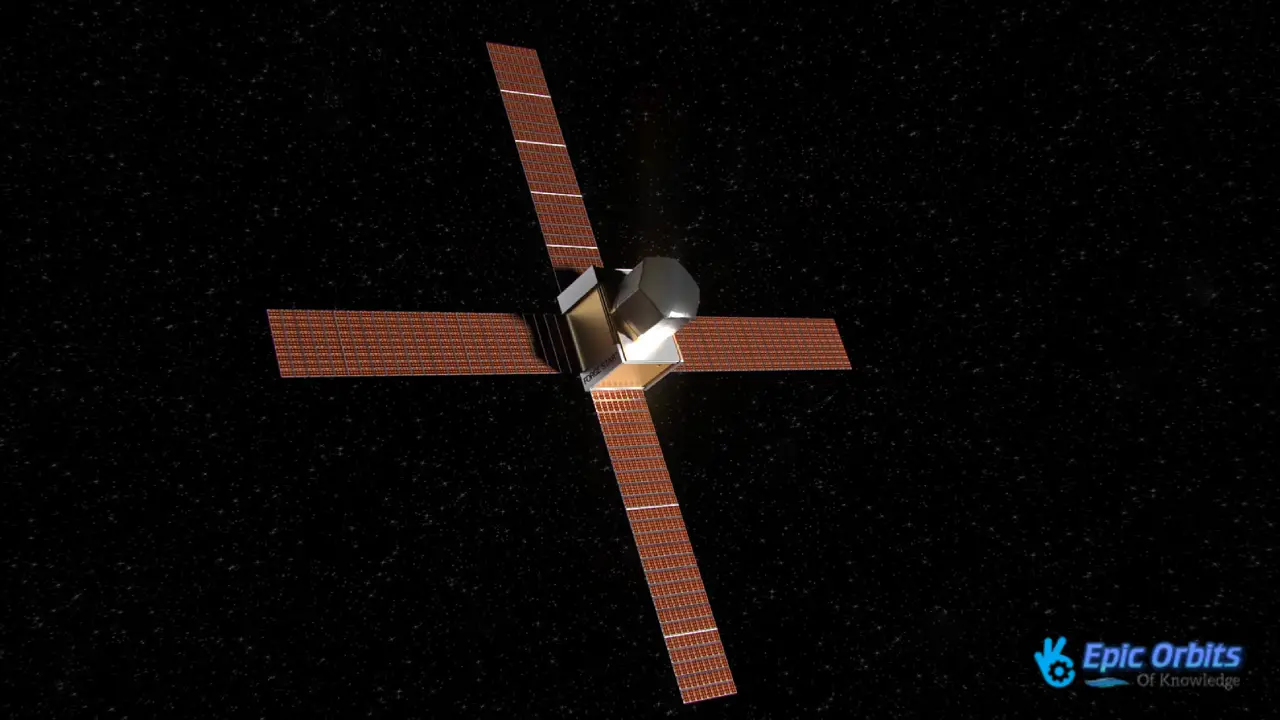

The ForgeStar satellite from Space Forge is a mini-factory that makes materials with qualities that can’t be made on Earth. It takes orbital manufacturing to the next level. The business is working on making super-materials like semiconductors and specific alloys that work better in microgravity, which might make them much more efficient. Space Forge’s business strategy is built on satellites that can be used again and again to make things in space for 10 days to 6 months at a time before coming back to Earth. This process creates an assembly line in space.
Companies like SpacePharma and Space Forge are changing the way we use space. They use the unique circumstances of orbit for research and production. As the cost of launching things into space goes down, space manufacturing becomes more economically viable. Such an endeavor might lead to a multi-billion dollar sector in only a few decades. These pioneering businesses are not only advancing our understanding of space but also paving the way for new sectors that have the potential to transform our lives.
Mining in space and using resources
Companies like AstroForge and Blue Origin are leading the way in space mining, which is a new area that is full of potential for giant profits. Space mining is one of the most ambitious commercial space endeavors, with corporations looking to the truly astronomical richness found in asteroids and lunar soil.
1. AstroForge: The First Company to Mine Asteroids
The only thing AstroForge, a US business, wants to do is mine asteroids. AstroForge is being careful since they’ve seen other space mining firms fail because they set their timetables too high. The first two missions are slated to begin in the coming year. The first will test extraction technologies using fake asteroid material, and the second will fly near a particular asteroid to discover more about what it’s made of.
A single asteroid with a lot of platinum might have more platinum group metals than have ever been mined on Earth. This could collapse the world market or make a firm more affluent than whole countries. AstroForge’s little flights are meant to test their mining method in space before they try to find particular asteroids, which is like making a cosmic assay office.
2. Blue Origin’s Blue Alchemist: Getting Resources from the Moon
Blue Origin’s Blue Alchemist technology takes a novel approach to space resources by exploiting elements that are already on the Moon instead of bringing them back to Earth. The business has shown that it can make solar cells and transmission lines out of fake lunar regolith. This might make it possible for future lunar outposts to generate electricity in a way that doesn’t harm the environment.

In-situ resource utilization (ISRU) is thought to be required for long-term space travel since sending what we need from Earth would be too costly. Jeff Bezos calls these technologies “the road to space” because they might one day let minerals mined in space remain there to construct infrastructure. These innovations would create a real space-based economy.
Managing Space Debris: Keeping the Orbit Clean
The buildup of space junk in Earth’s orbit is a big danger to working satellites and spacecraft. Over the years, people have sent thousands of satellites into space, which has unintentionally turned space into a junkyard with more than 36,000 pieces of trackable garbage and millions of smaller pieces of debris circling Earth.
This space junk is a big problem for active satellites and people flying in space. Even small paint specks, traveling at speeds of 17,500 mph, can cause significant damage, outpacing the speed of a bullet.
1. Astroscale: Experts in Cleaning Up Space
Astroscale is now the best company for collecting space junk. They make spacecraft that can catch and deorbit broken satellites before they break up into thousands of bits of junk. The company’s ELSA-d mission in 2021 proved the effectiveness of debris-capturing technology, paving the way for businesses to offer debris removal services.
Astroscale’s ELSA-M mission, which is set to launch in 2025, will improve on this technology with the goal of ultimately pulling dead satellites out of orbit. The business also plans to launch ADRAS-J, another spacecraft, in 2023. This spacecraft will take a closer look at junk in space.
2. Orbit Fab: Space Gas Stations
Orbit Fab is working on “gas stations in space,” which will let satellites recharge instead of becoming garbage when their propellant runs out. This is a new way to make space more sustainable. The company aims to establish its RAFTI (Rapidly Attachable Fluid Transfer Interface) as the standard fueling terminal for satellites in the future.
Orbit Fab’s fuel supply service is a fantastic deal at $20 million for 100 kg of hydrazine. It’s far cheaper than launching a whole new satellite. Active debris removal and satellite life extension are two ways to make space more sustainable. They demonstrate the growing recognition of orbital space as a finite resource requiring active management.
The Effect on the Economy of Private Space Companies
The private space business has a big effect on the economy. Experts predict that the value of the private space industry will reach $1 trillion by 2040. There are several things that are causing this expansion, such as new technologies, more investment, and the opening of new markets.
1. Making jobs and growing the economy
The commercial space sector has created tens of thousands of high-skilled jobs in engineering, manufacturing, software development, and operations. These jobs frequently pay far more than the national average, which helps the economy expand in the area. California, Texas, Florida, and Colorado are examples of “space hubs” where the sector tends to congregate. These areas become economic powerhouses.
- Through service industries and supply chains, space enterprises have created a lot of employment, both directly and indirectly.
- The economic effects go beyond direct jobs; each job in the space sector supports around 2–3 more jobs in the economy as a whole.
- Private space companies have brought in billions of dollars in investment funding. In 2021, more than $10 billion in private equity went to space entrepreneurs.
California hosts over 250 space companies, making it a significant contributor to the state’s GDP. Texas is home to more than 150 space companies, serving as a major economic driver in the region. Florida has over 100 space companies, playing a key role in the state’s economy.
2. Moving technology to other fields
A lot of the technology that was developed for space ends up in things we use on Earth, including memory foam mattresses and water purification systems. This transfer of technology adds economic value that is difficult to measure but greatly increases the return on investment in space technology.
Space commercialization has also opened up whole new sectors that didn’t exist previously, such as space tourism, satellite data analysis, orbital manufacturing, and debris cleanup services. Experts predict that these emerging markets will stimulate further economic growth and spark innovative concepts.
Problems That Private Space Companies Face
The private space business is at a crossroads, and firms are having a challenging time reaching their big ambitions. Even while private space firms have done some wonderful things, they face many problems that might stop them from reaching their goals.
1. International Space Law and Regulatory Hurdles
The rules for space operations are still complicated and broken apart, and corporations typically have to endure a lot of red tape from many government departments simply to have one launch permitted. Developed primarily during the Cold War, international space law never anticipated private enterprises mining asteroids or establishing settlements on Mars. Such an outcome leaves certain legal questions that might make it harder for people to invest. For example, there is still a lot of disagreement about who owns resources taken from celestial bodies. The 1967 Outer Space Treaty says that space is the “province of all mankind,” but the 2015 US Commercial Space Launch Competitiveness Act grants US citizens rights to resources they take.
2. Concerns About Funding and Long-Term Viability
Funding is always a problem, and many space projects need billions of dollars in upfront investment before they can start making money. Even the most imaginative investors may find this long wait period challenging. The space industry’s boom-and-bust cycles have caused several firms to go bankrupt, including Sea Launch and Firefly Aerospace (though the latter was subsequently brought back to life), showing how unstable the industry is. As competition heats up, businesses are under more and more pressure to show that they have sustainable business models that go beyond government contracts and venture funding. The situation shows that space is not simply a playground for millionaires but a real economic opportunity.
Furthermore, people are becoming more worried about the environment, both because of space junk and the carbon impact of regular launches. Some rockets release as much pollution as long-haul flights. Private space enterprises need to come up with new ideas and adapt to these problems by using technology and techniques that reduce their effect on the environment while still allowing for expansion.
The Future of Private Space Travel
As technology moves forward quickly, private space firms are ready to change the way we travel and explore space in the future. The following ten years will be crucial, with many new missions on the way.
The future of commercial space exploration seems bright, with firms pushing the limits of technology that was formerly only available to giant states. In the next 10 years, we could witness the first private crewed expeditions beyond Earth’s orbit, which might include flights around the moon.
If SpaceX’s Starship works, it will change how people can go to space by making launches a lot cheaper. This might make it cheaper to go to space than certain international shipping prices on Earth. Companies like Axiom Space are already working on building private space stations, and they want to build their own commercial stations.
There are plans for dozens of private trips to the Moon in the next five years, which will speed up lunar exploration by a lot. This will provide the groundwork for future lunar bases and resource use. Mars is still the goal, and SpaceX is sticking to its ambitious schedule for human trips.
The US Space Force is depending increasingly on commercial capabilities, which means that space militarization will continue to provide private corporations big contracts. Space tourism will grow from short trips to hotels in orbit and flybys of the moon.
The most important changes may come from places you wouldn’t anticipate, as lower launch costs make it possible to try out new technologies, experiments, and business models. Private firms have irreversibly changed the course of human space exploration. They have started a new space era characterized by commercial innovation and entrepreneurial vision.



